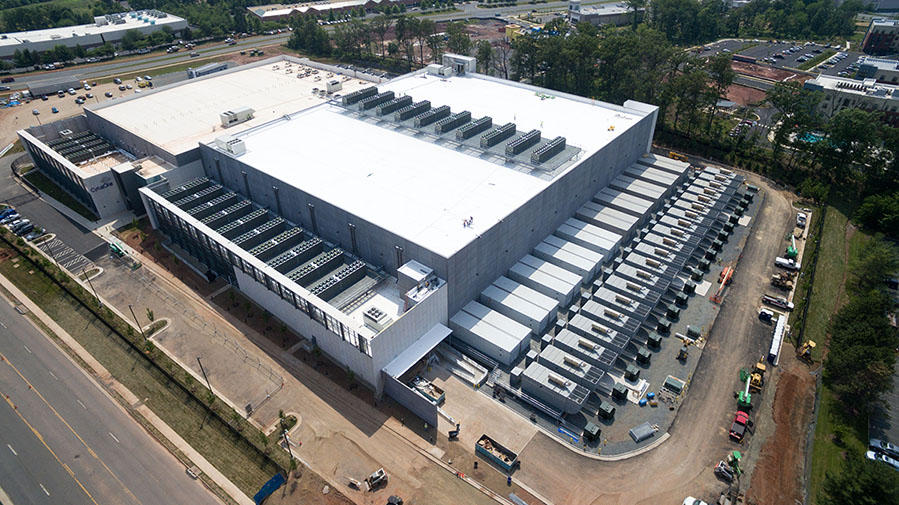

Data centers are technical facilities composed of networked computers and storages that are used by organizations to store, manage, disseminate and process large amounts of data. Data centers house even the most critical systems which are extremely vital for business continuity and operations, making its efficiency, security & reliability critically important for today’s businesses. The most important factor for any data center is ‘uptime’, which is its total operational / working time.
In this article, we are mainly going to have a quick look at the basic structure as well as fundamental details regarding data centers.
Data centers can be mainly classified into five types. They are:
- Enterprise Data Centers – Also known as Private Data Centers or In-house Data Centers. These data centers are built, maintained, owned and supervised by organizations for their specific needs only. Majorly, this type of data center is run and used by big enterprises; an organization’s own IT team manages these data centers.
- Managed Data Centers / Managed Service Providers – In this, there will be a third party called ‘Managed Service Providers’ who will help in managing the data center. These managed service providers will host another organization’s infrastructure services either in their own location / that organization’s location itself, as per requirements. Here, a part of the data center functions of an organization will be managed/controlled by a third party. Apart from that, vendor contracts / SLA’s are placed with the third party to ensure data safety. In this, the payment will go only / both for space as well as infrastructure management provided by the third party.
- Co-location Service Providers – Here, the server space is shared. In this case, data centers are hosted and maintained by a third party, but managed by the organization’s own employees. Thus, we can tell that co-location service providers will house and maintain the infrastructure of third parties via shared server space. The payment will go for the rack space consumed by the infrastructure equipments and not for the managed services.
- Multi-tenant Data Centers – Here, the user owns an entire set of racks, not a single rack. This will be costlier due to more power consumption and there will be a need for a defined lease-time for which rack space has to be booked. Payment will be done as per ownership, maintenance as well as management of the infrastructure provided.
- Public Cloud Providers – Also known as Cloud Data Centers. AWS, Microsoft Azure, etc. are examples. Every infrastructure needed will be hosted in the cloud, where payment will be done as per usage.
Choosing the right data center is very crucial to any business. Business houses decide upon this based on factors like cost, location / geographic restrictions, licensing, security, ownership, disaster recovery, availability of able staff and redundancy.
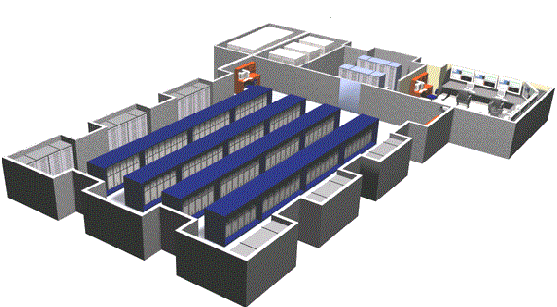
For the efficient operation and security of data centers, there are technical spaces/subsystems within them for ensuring robust Risk Management, Network Migration, Power Optimization, Thermal Efficiency as well as DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management). These subsystems are managed by the operational staff at the data centers.
Generally, these technical space/subsystems inside data centers are categorized as,
1) Physical Security Systems – A ‘six-layered approach’ has been adopted to ensure physical security within a data center. Data center buildings will be non-descriptive and modular in nature which will be divided into the following:
1)i. Perimeter – a particular area surrounding the data center building. The first level of defense.
1)ii. Clear zone – A protected area around the data center building as per the guidelines /rules of the respective
authority.
1) iii. Reception.
1) iv. Service corridor – an exclusive passage which is narrow compared to its own length; it will be exclusively used
for service purposes, to avoid any kind of delay as well as to cater to urgent requirements.
1) v. Data hall – The main, huge space in a data center where the data, i.e., the IT facilities for doing various
processes on these data are placed.
1) vi. Data cabinet – Also known as Data center rack. They provide airflow to keep things efficient and ensure that
cords, wires and other external items are not damaged via any kind of mistreatment. Thus, by protecting and
organizing technology, data cabinet ensures the security of data.
2) Network / IT and Structured Cabling Systems – Commence at the Entrance Service Facility (Telecommunications service entrance to the data center building; the backbone pathway between service provider & data center building.), to Main Distribution Area (MDA), from there to Horizondal Distribution Area (HDA) and then to Equipment Distribution Area (EDA).
2)i. MDA – where traffic from all areas of a data center converges; The central point of distribution for the data
center. Houses Core routers, PBX, Core LAN / Core SAN switches.
2) ii. HDA – houses cross connects as well as LAN/SAN switches for distributing cables to EDA.
2) iii. EDA – houses storage devices/application servers; Here, horizontal cabling is terminated at patch panels
Reception.
3) Intelligent Power Systems – Critical to the data center operations. Includes Medium Voltage Entrance Feed from the utility, Backup Generators, Battery Rooms, UPS Systems, Underfloor / Overhead Power Distribution, Cabinet-level Metered and Monitored PDUs, leading to Managed IT Equipment Power.
4) Environmental Control Systems – Starts with Chillar Plants, then leads to Computer Room Air Conditioning and Handling Systems, into the Data Hall with the mandatory flow for cooling via various cooling technologies as per the differing IT loads generating temperatures which need to be carefully managed.
5) Performance and Operational Management Systems – Does Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM). DCIM encompasses Asset Management, Power Monitoring, Environmental Monitoring, Change Management and Capacity Planning of a data center.
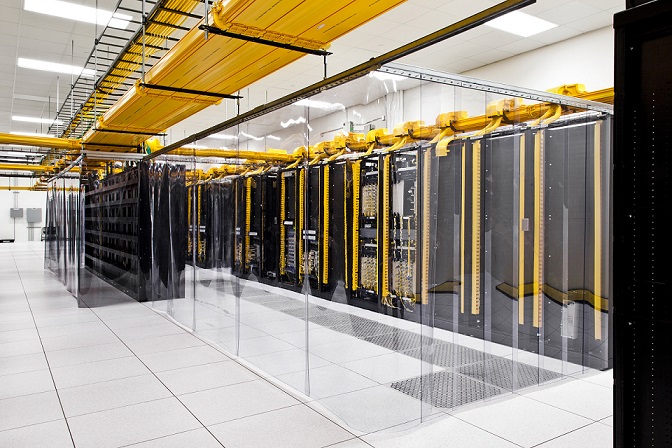

Data centers are giant buildings with row upon row of numerous IT systems, Power as well as Cooling working together to provide services which make businesses work. Efficiency, as well as the reliability of data centers are critically important in determining success of today’s businesses.
