AI, IoT, Bigdata, DevOps, Blockchain, Digital currency,… these are some of the IT buzzwords today. But as per our functional area/need, each one of us will be having different ideas about each of them. We, NODERICKS always have an eye for emerging & related technologies. Let’s have a look at each of them.
We can start with DevOps.
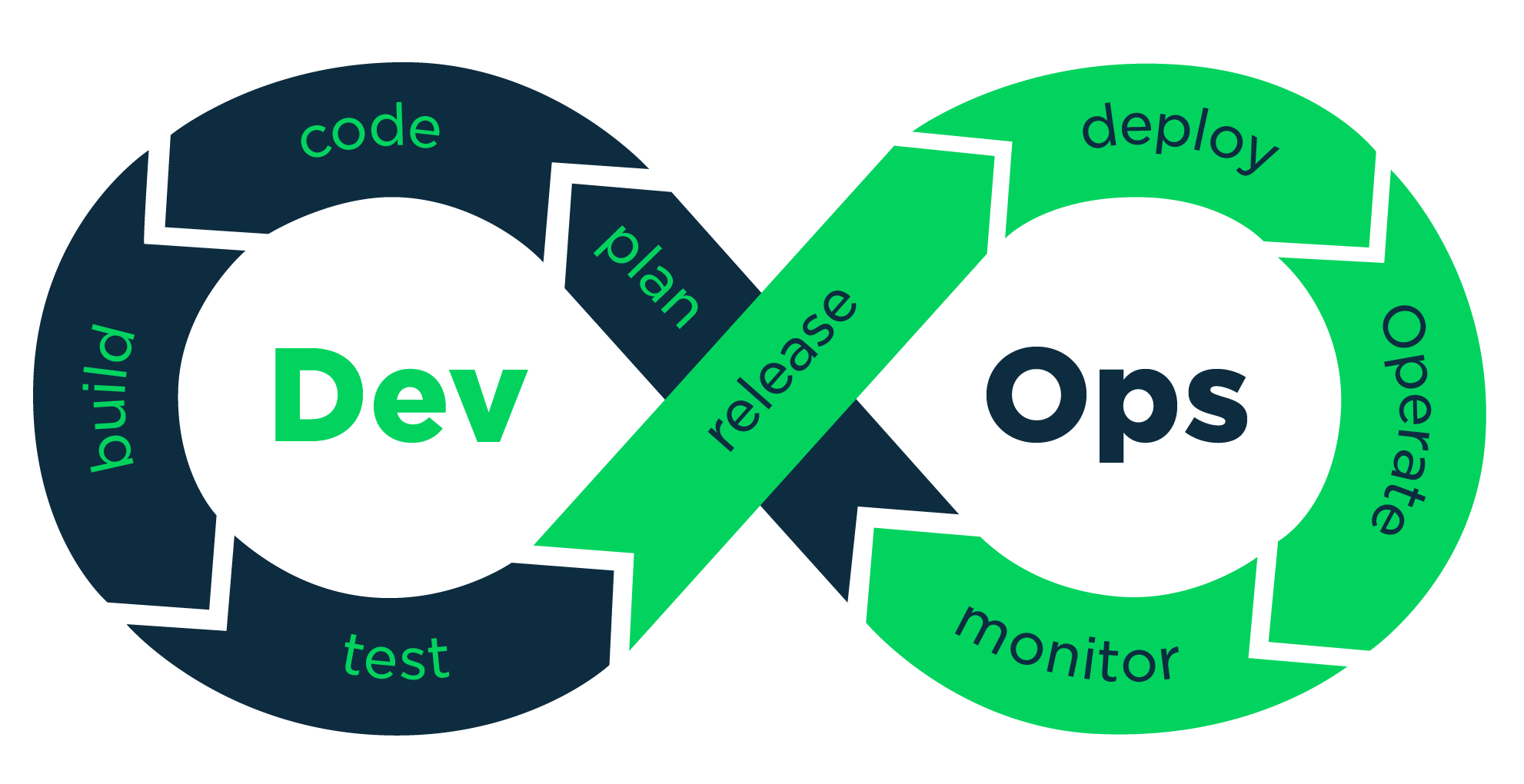
In agile methodology, delivery of a whole software application happens in smaller units. In this, requirements and its solutions evolve through the collaborative efforts by cross functional teams. Once the agile method got established, it gained higher software velocity & throughput. For more effectiveness, QA was also getting included in developer’s team, in agile. To further increase the software velocity, agile needed to encompass delivery as well as support teams. This, resulted in DevOps.
DevOps is a technology practice of unifying software development (Dev) and software operation (Ops). It incorporates automation as well as monitoring in every stage of software development. It is a process practiced by the developers as well as operations engineers right from the starting of the design to production support.
Without understanding DevOps Lifecycle, one cannot get clarity on DevOps. Majorly, DevOps Life cycle has the following 4steps.
Step I – Continuous Development: Here, the whole software development process is being divided into smaller development cycles. Development takes place simultaneously, to reduce the development time & for faster software delivery. This step includes coding; creating different forms of the code using SVN, Git, etc. & wrapping the code in an executable folder to send it to QA team for testing.
Step II – Continuous Testing: QA team conduct testing with respective tools. Multiple parts of the code will be tested continuously. On completion of testing, each of the parts will be getting integrated into the prevailing code.
Step III – Continuous Integration: In this step, any code producing a new functionality will get integrated to the prevailing code. This increases the importance of testing because this newly integrated code should not bring a negative reaction during runtime.
Step IV – Continuous Deployment: Software is deployed to the production house in this phase. All the developed code is deployed to the servers with 100% accuracy. Deployment is done continuously so that any changes made to the code at any time will not be affecting its run time, even in high traffic. So, during deployment, System administrators should keep on scaling up servers in order to withstand increased host users.
DevOps demand continuity & to make it work, there are DevOps platforms. It provides tools to store, version, build, test and release the application as well as infrastructure code via continuous delivery pipelines. There are hundreds of DevOps tools to help DevOps engineers to be productive. These tools possess relevant features, support several languages as well as Operating systems and, are highly secured. Depending on purpose, these tools are categorized into 5. They are,
i.Continuous Integration: Jenkins, Travis, TeamCity
ii.Configuration Management: Puppet, Chef, Ansible, CFengine
iii.Continuous Inspection: Sonarqube, HP Fortify, Coverity
iv.Containerization: Vagrant, Docker
v.Virtualization: Amazon EC2, VMWare, Microsoft Hyper-V
DevOps improves speed and quality of software delivery by encouraging communication, collaboration, integration and automation among software developers, QA and IT operation teams. When these teams work separately, developers will not get clarity on the roadblocks faced by QA & operations teams. QA & operation teams work on various features which may not have any context to the business value of the software, which is under construction. All these lead to inefficiency as well as finger pointing when something goes wrong. Ideally, DevOps addresses these issues by establishing collaborative cross-functional teams who share responsibilities.
